Post forecasts economic headwinds will continue to impact consumption of both pork and beef in 2024. Swine and pork production in 2024 will be marginally down 3 percent as persistently low live hog and pork prices weigh on producers. However, pork imports may grow marginally to offset the forecasted decline in domestic pork production. Beef imports in 2024 could decline due to the high year-end inventory carried over into 2024 and an expected flat demand. Both swine and cattle imports could also decline due to financial challenges among producers.
Swine Imports: Post revised up its forecast for swine imports in 2024 to 7,000 head based on higher-than-expected imports in 2023 despite difficult financial conditions for swine producers. Imports should still decline in 2024 from 2023 as financial difficulties and low prices continue to weigh on producers.
Pork Imports: Post forecasts pork imports in 2024 to grow marginally as imports offset the decline in domestic pork production.
Cattle Imports: Post's forecast of cattle imports in 2024 remains the same with official USDA forecast at 125,000 head with a significant decline due to shrinking profits of beef cattle producers in 2023.
Beef Imports: Post revised its forecast of beef imports in 2024 down to 3.4 MMT with a decline of 5 percent due to a high year-end inventory carried over into 2024 and flat demand in 2024.
SWINE
Live Swine Imports to Remain Low
Post revised up its forecast for swine imports in 2024 to 7,000 head, but imports will still moderately decline from 2023 (see Chart 1). China imports breeding swine to improve domestic herd genetics. Imported live swine only account for around 0.001 percent of the total swine population. Most swine producers continue to be under financial pressure, making it difficult to invest in herd improvements. Additionally, despite the falling sow and swine inventory, current sow levels are above the Peoples Republic of China's (PRC) official targets. Industry contacts also believe current sow levels are sufficient.
The main suppliers of live swine to China are the United States, Denmark, and France as they have different competitive advantages on litter size, body shape, lean meat rate, growth rate, and disease resistance. According to industry sources, swine from Denmark have the highest number of pigs per litter but lower PSY. Swine from the United States generally have larger body sizes, swine from Canada have good litter sizes, and swine from France have a good balance of growth rate and disease resistance.
Chart 1. China: Live Swine Imports
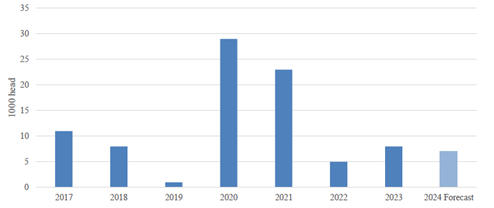
Source: Trade Data Monitor, LLC and Post Forecast
Post revised swine imports up in 2023 to 8,000 head compared to 5,000 head in 2022 according to data from Trade Data Monitor (TDM). The surge in swine imports in 2020 and 2021 were from large swine producers rebuilding their herds following the outbreak of ASF. Imports dropped significantly in 2022 once herds returned to pre-ASF levels but returned to 2018 levels in 2023 as larger producers, the main importers of live swine, gained more market share and pushed out smaller producers.
PORK
Minor Growth in Pork Imports
Post revised its forecast for 2024 pork imports down to 1.95 MMT; however, pork imports will have minimal YOY growth (see Chart 2). Post projects the pork market to remain relatively weak in 2024, thus curbing further growth for imported pork. Additionally, high year-end inventories carried over into 2024 will suppress imports until traders diminish their supplies in their full coastal cold storage facilities. Industry sources indicate that the majority of active pork traders are larger importers since smaller traders find the pork sector too risky at the moment. China's major pork suppliers are Spain, Brazil, Denmark, the Netherlands, Canada, and the United States.
Chart 2. China: Pork Imports
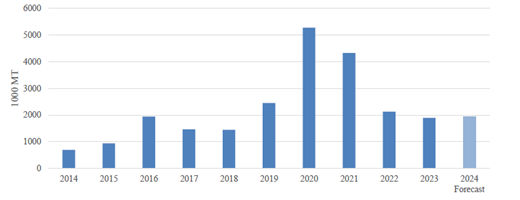
Source: Trade Data Monitor, LLC and Post Forecasts
Post revised pork imports in 2023 down to 1.90 MMT with a 11 percent decline YOY according to TDM. Importers imported more in the beginning of the year as they believed the market in 2023 would recover after the PRC lifted COVID lockdown restrictions. However, due to a large domestic production and a slower-than-expected economic recovery, imports gradually slowed throughout 2023 (see Chart 3). Sources also indicated that traders had higher stocks in their coastal storage facilities at the end of 2023 than they did at the end of 2022.
Chart 3. China: Monthly Imports of Pork Products
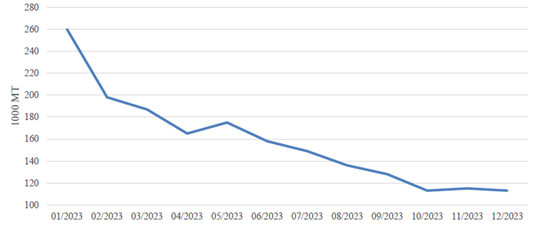
Source: Trade Data Monitor, LLC
CATTLE
Cattle Imports to Decline
Post's forecast of cattle imports in 2024 remains the same with the official USDA forecast at 125,000 head. The significant decline in imports from the highs in 2021 and 2022 (see Chart 4) are due to shrinking profits of beef cattle producers in 2023.
Chart 4. China: Live Cattle Imports
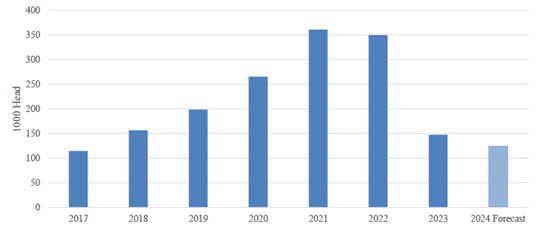
Source: Trade Data Monitor, LLC and Post Forecast
Beef cattle prices witnessed a sharper decline than beef prices in 2023. Beef cattle producers are still profitable, but their profit margins were much narrower than in 2022. Dairy cattle producers are in a similar situation but facing even lower margins. China mainly imports live cattle for breeding purposes. Post forecasts lower live cattle imports in 2024 as most cattle producers are less motivated to expand their herds or improve herd genetics with imported live cattle in such difficult market conditions.
Another factor, less important than the economic headwinds facing the industry, that contributes to lower imports of beef cattle is the lack of farm management experience. China mainly imports beef cattle breeds of high quality, such as Angus, for high-end beef cattle breeding and to improve their herd genetics. Sources commented that due to challenges of farm management, some imported beef cattle did not reach their optimal carcass weights, which discouraged some producers from importing more beef cattle.
Australia is China's top supplier for dairy cattle, while Uruguay and Chile are China's main beef cattle suppliers. Although Myanmar regained market access for beef in 2023, Myanmar cattle exports will not have a noticeable impact on overall imports.
Post revised its 2023 cattle import number to 148,000 head, down 58 percent due to the weak beef cattle market, according to TDM.
BEEF
Beef Imports to Decline
Post revised its forecast of beef imports in 2024 down to 3.4 MMT with a decline of 5 percent (see Chart 5) due to the high year-end inventory carried over to 2024 and expected flat demand.
Chart 5. China: Beef Imports
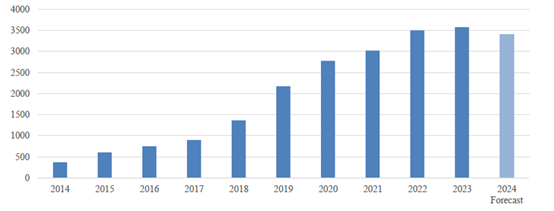
Source: Trade Data Monitor, LLC and Post Forecast
China witnessed a 10-year-high in beef imports in 2023. Imports were strong in the first 8 months of 2023 before they slowed down (see Chart 6). Sources indicated importers imported more in early 2023 to stock up in anticipation that the post-COVID market would be better. However, in 2023, the market for beef did not recover from the pandemic as much as importers expected. Beef imports started to slow down in the second half of 2023 as inventory started to accumulate, which will negatively impact imports in 2024.
Chart 6. China: Beef Monthly Imports
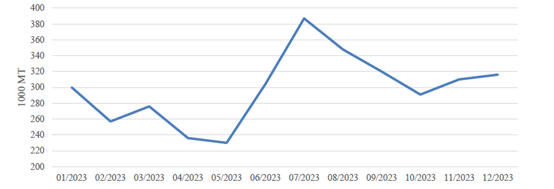
Source: Trade Data Monitor, LLC
In 2024, with flat demand and consumption downgrading, lower-priced grass-fed beef imported from Brazil, Uruguay, and Argentina (see Chart 7) may find more opportunities. Higher-priced imported beef products, on the other hand, may face more challenges in 2024. Industry contacts also indicated Chinese importers prefer certain cuts that are different from the standard cuts from other countries. Brazil, for instance, has better adapted to China's cutting standard due to competitive labor costs. U.S. beef and beef products are functionally subject to the most-favored-nation (MFN) tariff rates as importers have been able to apply for exemptions from Section 301 tariffs. Australia, New Zealand, and Chile have free trade agreements with the PRC; therefore, their beef and beef products tariffs have been reduced to zero.
Chart 7. China: Imported Beef Prices in 2023 by Supplier
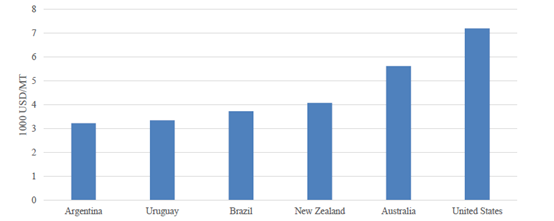
Source: Trade Data Monitor, LLC
In 2023 and early 2024, the PRC granted/resumed beef and beef products import access to several countries, such as Colombia, Poland, and Spain. The beef volume available from these countries to export to China is limited; therefore, post projects that these market access developments will have a negligible effect on China’s overall 2024 imports.
One factor that could influence import volume is speculation. As China is still a developing market for beef traders, some traders speculate in the market, disregarding real demand and drive-up import volumes. There have been speculative periods in the past and this could continue in 2024 as the market remains choppy.
Post revised the 2023 beef import number with a 2 percent growth according to TDM. As for reasons for the import growth, in addition to the factors discussed above, import price was also a factor. In 2023, the average importing price declined 25 percent YOY. China continues to import split carcasses from grass-fed beef producing regions in South America whose cost of production is cheaper than domestic production. Beef processors in China import split carcasses and then process them according to Chinese standards. In the price sensitive beef market of 2024, the trend of importing price competitive grass-fed split carcasses will increase.
Please click READ MORE to access the report.
Source: USDA
Note: This article is compiled by Antion. Please indicate the source for reprint.