The development of food science and technology and industry and the globalization of trade have promoted the diversity of food sources on the Chinese market. One of the more obvious trends is the increasing globalization of the supply of food and ingredients. The types and sources of food ingredients are also expanding. Some food ingredients that do not have traditional dietary habits in China are gradually coming to the consumers. In order to regulate the development and application of food ingredients and ensure food safety, these ingredients must be declared and evaluated for novel food ingredients before put on the market for sale. Only after approval by the National Health Commission (hereinafter referred to as NHC) can they be sold. To promote enterprises' understanding of novel food ingredients and avoid food compliance issues, this passages introduces China's novel food ingredients management system.
1. Introduction of Novel Food Ingredients
The term "novel food ingredients" was formerly known as new resource foods, and it originally came from Article 22 of the "Food Health Law (Trial)" issued by China in 1983 ("Produced food using new resources must be approved by the Department of Food Health" ), thereby the basic management system for new resource foods was preliminarily determined. Since then, the expression "novel food ingredients" was used in Article 44 of the Food Safety Law issued and implemented in 2009. In 2013, with the issuance and implementation of the "Administrative Measures on the Safety Review of Novel Food Ingredients", "New Resource Food" was officially renamed as "Novel Food Ingredients" which was continued to use until now. At present, the current "Administrative Measures on the Safety Review of Novel Food Ingredients" has been implemented for nearly 13 years. It is predicted that the relevant laws and regulations on novel food ingredients will also be revised in the future, and the detailed management system and regulations will be further clarified, and check for gaps.
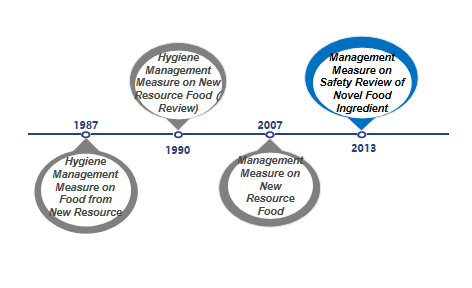
Source: Antion
Figure 1: Development of novel food ingredients regulations
From 1987 to 2007, both final food products and food ingredients can be classified according to the new resource foods. With the update of management regulations, since December 2007, the management objects of such regulations have been limited to food ingredients. In addition, the definition and scope of such ingredients have also gradually been clarified and refined. At the same time, with the improvement of relevant management regulations, the currently effective "Administrative Measures on the Safety Review of Novel Food Ingredients" also clarifies four types of non-novel food ingredients that do not meet the declaration requirements: 1. Substances that do not have the characteristics of food ingredients; 2. Substances that have been listed in GB 2760 and GB 14880 (ie food additives and nutritional fortifiers); 3. Substances that the NHC has issued to have no administrative permission; 4. Other substances that do not meet the requirements of relevant laws and regulations.
From the perspective of approval, from 2008 to 2019, the total number of novel food ingredients approved was 130 (Figure 2 for details and Table 1 for the list of approved ingredients).
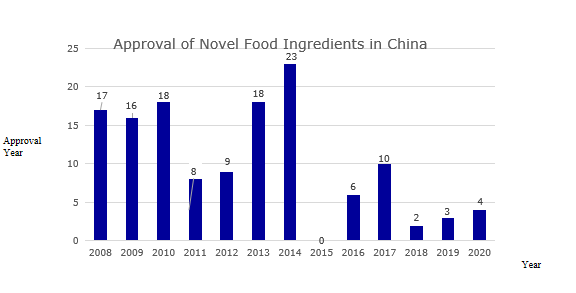
Source: Antion
Figure 2: Approval of novel food ingredients in China over the years
Table 1: List of novel food ingredients approved by China over the years
Year | Name of novel food ingredients |
2008 | Lactobacillus acidophilus (strain number: DSM13241), sodium hyaluronate, lutein ester, L-arabinose, Acanthopanax senticosus, aloe vera gel, galactooligosaccharides, Lactobacillus paracasei (strain number : GM080, GMNL-33), Lactobacillus acidophilus (strain number: R0052), Lactobacillus rhamnosus (strain number: R0011), hydrolyzed egg yolk powder, isomalt, Lactobacillus plantarum (strain number: 299v) , Lactobacillus plantarum (strain number: CGMCC NO.1258), plant stanol esters, oligosaccharides, bead peptide powder |
2009 | Cordyceps militaris, inulin, polyfructose, γ-aminobutyric acid, colostrum basic protein powder, conjugated linoleic acid, conjugated linoleic acid glyceride, Lactobacillus plantarum (strain number: ST-Ⅲ), Eucommia Seed oil, tea seed oil, salt algae and extract, fish oil and extract, diglyceride oil, earth protein, milk mineral salt, milk alkaline protein |
2010 | DHA algae oil, cottonseed oligosaccharides, phytosterol esters, phytosterols, arachidonic acid oils, Chinese cabbage, royal rice oil, golden tea, Xianmai vortex flower (small black medicine), noni pulp, yeast β-glucan, snow lotus culture, sucrose polyester, corn oligopeptide powder, phosphatidylserine, Haematococcus pluvialis, epigallocatechin gallate, Propionibacterium fischeri subsp. |
2011 | Samara oil, β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyric acid, ingot maple seed oil, peony seed oil, maca powder, Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis, Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis, Lactococcus lactis diacetyl subsp |
2012 | Mussel polysaccharides, medium-long chain fatty acids, wheat oligopeptides, ginseng (planted), Chlorella protothecoides, medicinal leaves, Moringa oleifera leaves, sucrose polyester, Leuconostoc mesenteri subspecies |
2013 | Camellia sinensis, Suaeda salsa seed oil, American vine fruit oil, salt shea butter, Guangdong Cordyceps fruiting body, acai fruit, tea mycelia leaf layer layer fermented mycelium, Euglena, 1,6-bis Trisodium Fructose Phosphate, Danfeng Peony Flower, Narrow-line Grain Tea, Almond Oil, Almond-tree Fruit Oil, Green Willow Leaf, Mannose Oligosaccharides, Serpentine Grape Leaf, Krill Oil, Max Kluyveromyces |
2014 | Chitooligosaccharides, Silybum marianum seed oil, Willow oleracea, Eucommia ulmoides, gorse, gypsum, tagatose, chia seeds, psyllium husk, Lactobacillus reuteri (strain number: DSM17938) , Cordyceps militaris, phytostanol ester, tea theanine, tomato seed oil, loquat leaf, arabinogalactan, Hubei Begonia (tea begonia) leaf, bamboo flavonoids, oat β-glucan, Lactobacillus sake , Propionibacterium propioni, xylooligosaccharides (adjusted), Pediococcus lactis, Pediococcus pentosaceus |
2015 | nothing |
2016 | Staphylococcus carnosus, Lactobacillus fermentum (strain number: CECT5716), Bifidobacterium breve (strain number: M-16V), Bacillus coagulans, Staphylococcus calves, Staphylococcus xylose |
2017 | Shea butter, (3R,3'R)-dihydroxy-β-carotene, Bole fruit powder, N-acetylneuraminic acid, cis-15-tetracosenoic acid, broccoli seed water extract , Rice bran fatty alkanol, γ-linolenic acid oil (derived from Cunninghamella echinulata), β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyric acid calcium, Mujiangye Ke |
2018 | Black fruit gland rib tree fruit, Candida globosa (Gexian rice) |
2019 | Lactobacillus curvatus, Ashitaba, loquat flower |
2. Requirements for New Food Ingredients Declaration Materials
If the ingredients used by the enterprise meet the definition of novel food ingredients, the ingredients need to be declared as novel food ingredients before using. According to the requirements of the "Novel Food Ingredients Declaration and Acceptance", the materials required for the application of novel food ingredients are as follows (specific details to be determined according to different types of ingredients).
(1) Application form
(2) Research and development report of novel food ingredient
(3) Safety assessment report
a) Composition analysis report
b) Hygiene inspection report (qualify required)
c) Toxicology evaluation report
(There are qualification requirements, the test items are determined by the using conditions of domestic and foreign countries, and the number of items ranges from 2 to 7)
d) Microbial resistance test and toxicity test (qualify required, only for microorganisms)
e) Safety evaluation opinions
(The basic information of the declared substance, composition analysis, toxicology data, population data, consumption and using status and intake assessment and other information need to be written by the organization that meets the qualification requirements)
(4) Production process
(5) Product related standards
(6) Product label and instructions
(7) Status of application domestic and overseas and related safety assessment documents
(8) Certification of attorney (if attorney existed)
(9) Other materials helpful to review and evaluation
(10) Sealed product sample or 30-grams of raw material
In addition, if the declared substance is imported, the following documents are also required.
(11) Materials to be submitted for imported novel food ingredient
a) Certificate or document that allows the material to be produced or sold in the country (territory) of origin issued by relevant departments or organizations of the exporting country (territory)
b) Certificate or document that proves the manufacturer is audited and qualified, issued by relevant departments or organizations of the country (territory) where the manufacturer is located
3. Novel food ingredient approval process
The specific approval process for novel food ingredients can be seen in Figure 3.
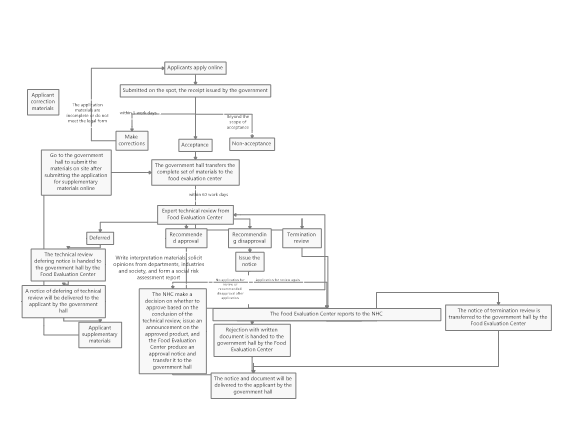
Source: Reference to the official website of the NHC
Figure 3: Work flow chart of administrative license for novel food ingredients approval
4. Review conclusion
As seen from Figure 3, the review conclusions of the novel food ingredients are divided into four situations, which are postponed re-examination, recommended approval, recommended disapproval and termination of the review. The specific explanations for these situations are as follows.
Postponed re-examination
If the submitted application materials need to be modified or supplemented, or if further verification tests or scientific demonstrations are required, the NHC shall issue the "Notice of the Administrative Licensing Technical Review Extension". The applicant shall supplement and submit the missing application materials according to the notice, then conduct another expert review.
Recommended approval
If the declared substance passes the review of the expert organization and the review conclusion is "Recommendation Approval", the NHC will solicit opinions from the society for 30 days. After that, the NHC will make an analysis on the opinions, and finally issue the "Notice of Administrative License Review Conclusions".
Recommended disapproval
If the declared substance does not meet the definition of novel food ingredients(e.g., it does not have the characteristics of novel food ingredients), or does not meet the required nutritional requirements, or the safety cannot be guaranteed, the technical review conclusion will be "recommended disapproval". The NHC will issue the "Notice of Opinion on Technical Review of Administrative Licensing" to the applicant. If the applicant disagrees with this conclusion, an application for review again can be submitted within 30 days. If the conclusion after review again is still "recommended disapproval", or if the application for review again is not submitted within the limited time, the NHC will issue the "Rejection with written document" to the applicant and inform the reasons for disapproval.
It should be noted that if the application materials or samples are not true, it will also cause "recommended disapproval". In addition, according to the above definition of non-novel food ingredients, substances that do not have administrative permission cannot be declared novel food ingredients again.
Termination review
If the declared substance is common food ingredient, or is substantially equivalent to the common food ingredient or the approved novel food ingredient, the NHC will issue an "Administrative License Termination Review Notice" to the applicant and inform the reason.
The word“substantial equivalence”comes from the New Resources Food Management Measures in 2007, which refers to, for example, a newly declared food ingredient and food or a new published novel food ingredient in terms of species, source, biological characteristics, main constituents, edible parts, amount of use, range of use and application group are the same. The process and quality requirements used are basically the same, which can be considered to be equally safe and substantial equivalent.
Reference
Food Safety Law
New Resource Food Management Measures
Administrative Measures on the Safety Review of Novel Food Ingredients
Novel Food Ingredients Application and Acceptance
Administrative Measures of Safety Evaluation for Novel Food Ingredient
Antion can provide guidance and technical support for the whole process of Novel Food Ingredient Application, including regulation monitoring and interpretation, application material composing and review, test arrangement, authorities communication, etc. If you have any questions, please feel free to contact us: Lillian.fan@antion.net
Relevant Reading:
Introduction of Food Related Application & Registration Services